Transparency First
Then Trust
The world needs
more transparency
in the cybersecurity
Ensuring the protection of data and systems from potential damage is a fundamental aspect of cybersecurity. It is challenging for customers to select a product if they do not have the opportunity to verify whether the software aligns with specific standards. The multibillion-dollar endpoint cybersecurity industry is characterized by the absence of standardized policies, despite its global impact on businesses.
Endpoint security software is designed to minimize risk. A beneficial approach to ensuring user understanding of a developer’s role in mitigating risk is through transparency of the application’s functionality and the developer’s infrastructure processes. By disclosing certain statistical information, it is possible to identify and understand the strengths of a product. This strategy has the potential to address the underlying issue, leading to the elimination of all remaining gaps. Conversely, developers who opt for the more challenging approach of disclosing statistical data from end devices may encounter public criticism and oversight. However, this approach is ultimately beneficial for all companies and institutions.
In the context of business-to-business relationships, clear guidelines are essential for fostering mutual trust. The cybersecurity industry should adopt a transparency approach to bolster the trust end customers place in those responsible for their brand’s image. This approach is instrumental in fostering collective progress in the realm of cybersecurity.
What is this audit?
Definition of "Cyber Transparency Audit"
As part of the “Cyber Transparency Audit,” the testing body, in the role of the Auditor, verifies data from a cybersecurity solution provider to ensure historical compliance.
The audit is a formal evaluation of a system, organization, process, or project. The data is examined to ensure compliance with specific guidelines. The primary benefit of conducting the audit is the involvement of an external Auditor, who can meticulously assess and impartially identify areas that require enhancement.
Obtaining the “Cyber Transparency Audit – Certified” certificate by a provider means that its effectiveness regarding historical data is confirmed.
The methodology and policy are available to anyone who meets the specified criteria. Therefore, anyone is welcome to join the project as an auditor or developer.
Security incidents in telemetry data
This report contains analyzed and anonymized telemetry data from devices protected against malicious software by a product called Xcitium Advanced. The data show a correlation between potentially malicious activity on a Windows device and confirmed malware. This is significant because unknown files on employees’ computers that have not yet been confirmed as malware can serve as a backdoor to serious threats, such as ransomware or spyware.
After reviewing the historical data, we can confirm that from September 30, 2024, to December 29, 2024, among 1,051,109 unknown 0-day files, no malware infection was recorded on systems protected by Xcitium software.
Key audit insights
- Audited period: September 30, 2024 – December 29, 2024
- Purpose of the audit: Confirmation of compliance with data from the audited period, indication of key information about malware and data leaks.
- Scope of the conducted audit: Audit of telemetry data concerns devices protected by the developer's software and file metadata as part of access to its static threat infrastructure.
- Name of the audited developer: Xcitium
- Data comes from software of the class: EDR, XDR, MDR Xcitium. The developer did not disclose which operating systems the audited period covers. Based on the audited file extensions for malware and clean samples, we conclude that this is a Windows environment.
-
Public Data:
https://www.xcitium.com/resources/threat-labs/data-statistics/
https://verdict.xcitium.com/
The audit was prepared taking into account the following data set
- Devices with potentially malicious activity (virtualized files).
- Devices with confirmed malware status (virtualized files).
- The number of 0-day files classified as secure.
- Number of 0-day files classified as PUAs.
- Number of 0-day files classified as malware.
- Potential data leaks and active infections.
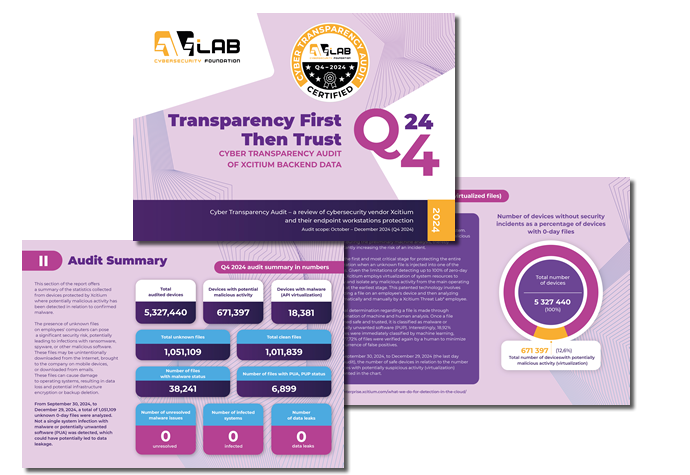
Audit summary
This section of the report offers a summary of the statistics collected from devices protected by Xcitium where potentially malicious activity has been detected in relation to confirmed malware. This activity has been linked to the uploading of a file from a device for analysis in the cloud.
The presence of unknown files on employees’ computers can pose a significant security risk, potentially leading to infections with ransomware, spyware, or other malicious software. These files may be unintentionally downloaded from the Internet, brought to the company on mobile devices, or downloaded from emails. These files can cause damage to operating systems, resulting in data loss and potential infrastructure encryption or backup deletion.
From September 30, 2024, to December 29, 2024, a total of 1,051,109 unknown 0-day files were analyzed. Not a single system infection with malware or potentially unwanted software (PUA) was detected, which could have potentially led to data leakage.
Q4 2024 Audit Summary in Numbers
Total
audited devices
Devices with potential malicious activity
Devices with malware
(in containment)
Total unknown files
Total clean files
Number of files with malware status
Number of files with PUA, PUP status
Number of unresolved malware issues
Number of infected systems
Number
of data leaks